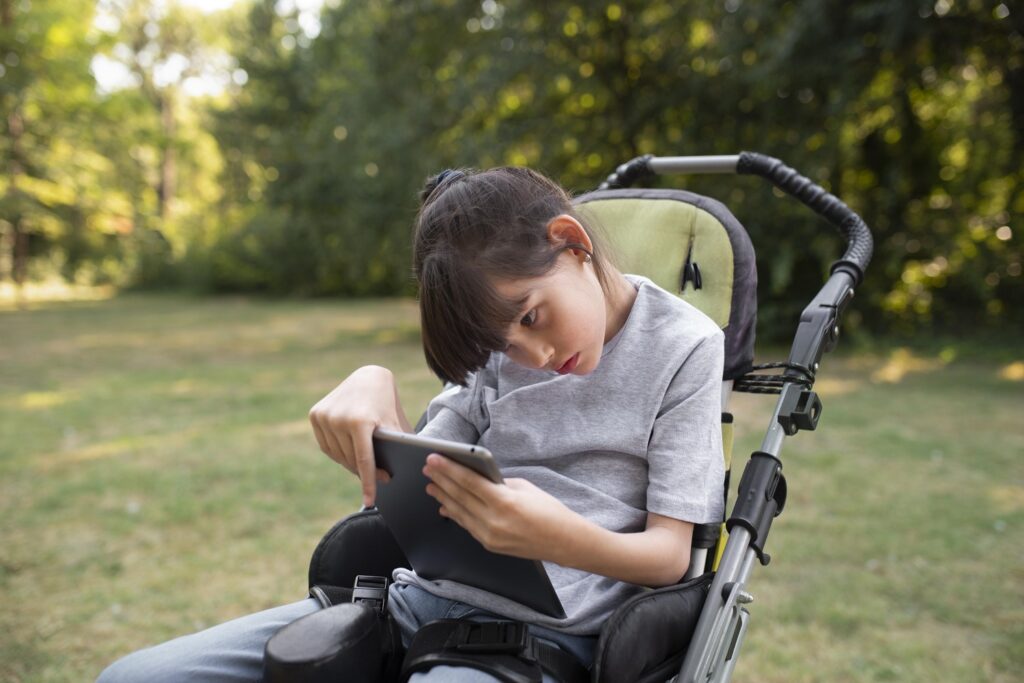

Cerebral Palsy:
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a non-progressive neurological disorder that affects the brain and musculoskeletal system. It typically results from brain damage occurring before, during, or shortly after birth. CP is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders in children and is categorized into different types based on specific neurological symptoms. Children with CP often experience difficulties with motor skills, including coordination, balance, walking, standing, speech, eating, and controlling bladder and bowel functions. This condition cannot be cured completely, although treatment and therapies can help improve the condition make them maximize in their daily activities.
Hemiplegia And Hemiparesis:
Hemiplegia, derived from “hemi” meaning half and “plegia” meaning paralysis, refers to paralysis affecting one side of the body—typically involving the lower face, arm, and leg. In addition to motor impairments, individuals may also experience loss of sensation, memory, cognitive function, as well as bowel and bladder control. The most common cause of hemiplegia is a stroke, which damages the corticospinal tracts in one or both hemispheres of the brain. Other potential causes include traumatic injuries (such as spinal cord damage), brain tumours, and infections of the central nervous system (CNS).
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause and using various therapeutic approaches to restore motor and sensory function. Physical therapy plays a key role in improving movement, especially in the affected limbs, with techniques such as Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (MCIMT) and mirror therapy.
The terms hemiplegia and hemiparesis are often used interchangeably, as both involve similar symptoms, though hemiparesis generally refers to weakness rather than complete paralysis. Individuals with hemiparesis experience muscle weakness on one side of the body, which can interfere with daily activities. In some cases, they may also have difficulty with breathing, swallowing, and speaking.

